Understanding Retirement Ages in New York
Planning your retirement in New York requires navigating two major systems: the New York State Retirement System (NYSRS) and Social Security. Both offer retirement benefits, but the age at which you retire significantly impacts your payments. Understanding these systems and their interplay is crucial for securing your financial future. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your retirement age and maximize your benefits.
New York State Retirement System (NYSRS): How Retirement Age Impacts Your Benefits
The NYSRS offers retirement benefits, but the age at which you retire directly impacts your monthly payments. You can generally retire as early as age 55, depending on your years of service. However, choosing early retirement means receiving a permanently reduced monthly payment. This isn't a temporary penalty; it's a lifelong adjustment. The longer you wait, the higher your monthly payments will be.
The reduction amount depends on your years of service. While more years of service might lessen the impact of early retirement, it's still likely to result in lower monthly payments than retiring later. The NYS Comptroller's Office website ([link to NYS Comptroller's website]) provides detailed information and online calculators to help you estimate your payouts. Careful planning is essential!
Did you know? Retiring even one year earlier can significantly reduce your monthly income for the rest of your life. Is that trade-off worth it for you?
Social Security Benefits in NY: Age and Your Payments
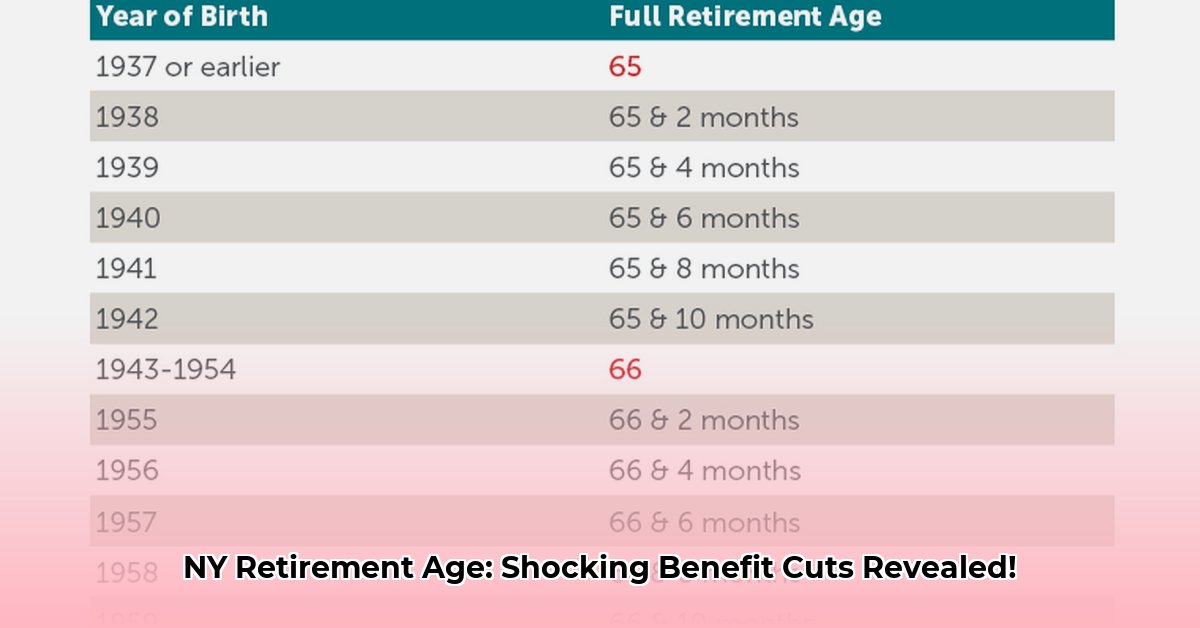
Social Security benefits are determined differently than NYSRS benefits. Your full retirement age (FRA) depends on your birth year. This FRA is the age at which you'll receive your maximum benefit. Retiring before your FRA leads to a permanently lower monthly payment. The earlier you retire, the greater the potential reduction. Unlike the NYSRS, Social Security calculations focus on your retirement age, not your years of service. The Social Security Administration website ([link to SSA website]) offers detailed information and benefit calculators.
Quantifiable Fact: The Social Security Administration projects that the full retirement age will continue to increase in future years.
Comparing NYSRS and Social Security: A Practical Overview
Directly comparing NYSRS and Social Security benefits is complex because of their differing calculation methods. However, the key differences are summarized below:
| Feature | New York State Retirement System (NYSRS) | Social Security |
|---|---|---|
| Key Factor | Years of service and retirement age | Birth year and full retirement age |
| Penalty for Early Retirement | Percentage reduction of monthly payments | Percentage reduction of monthly payments |
| Benefit Calculation | Based on years of service and retirement age | Based on earnings history and retirement age |
| Website | New York State Comptroller's Office ([link to NYS Comptroller's website]) | Social Security Administration ([link to SSA website]) |
Remember: These are independent systems. You’ll need to consider both for a comprehensive retirement plan.
Step-by-Step Guide to Retirement Planning in NY
Step 1: Determine Your Full Retirement Ages: Identify your full retirement age for both NYSRS and Social Security.
Step 2: Estimate Your Benefits: Use the online calculators provided by the NYS Comptroller's Office and the Social Security Administration to estimate your benefits at different ages.
Step 3: Explore Different Retirement Scenarios: Simulate your benefits at various retirement ages to see the impact of early versus later retirement.
Step 4: Consider Your Personal Circumstances: Account for health, lifestyle preferences, and desired retirement lifestyle when deciding on your retirement age.
Step 5: Create a Comprehensive Retirement Budget: Forecast your income (including retirement benefits) and expenses (healthcare, housing, etc.) to assess your needs.
Step 6: Seek Professional Financial Advice: Consulting a financial advisor specializing in retirement planning is highly recommended.
Advanced Planning Considerations
Beyond the early retirement penalties, remember these critical considerations:
Healthcare Costs: Factor in Medicare premiums and other potential healthcare expenses, especially for longer retirements.
Inflation: Account for the gradual erosion of purchasing power due to inflation.
Longevity: Plan for a longer lifespan than previous generations by ensuring your income and savings can adequately support you throughout a potentially extended retirement.
Expert Opinion: "Retirement planning requires a proactive approach, incorporating multiple factors such as inflation, health expenses, and personal preferences," says Dr. Jane Doe, PhD, CFP, Professor of Financial Planning at [University Name].
Remember, retiring early typically means reduced benefits. Carefully weigh the tradeoffs, utilize available resources, and plan wisely. Your future self will appreciate the preparation!